Hosting a Jekyll Site in S3 Part 2
In Part 1 resources were created to host the Jekyll site in S3 using Terraform
Now let’s setup the git repo and gitlab server to automatically push changes to the site to S3.
Setup git repo
Steps to setup git repo to build and deploy new jekyll site contents during every new git push into gitlab.
Create a .gitlab-ci.yml file in the root of the repo.
This will:
- Build the Jekyll site using the gitlab-runner and bundle it for deployment.
- Use aws cli to deploy the Jekyll site contents to S3
- Invalidate the cloudfront distribution to refresh all the contents
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
image: ruby:3.3
stages:
- build
- deploy
build:
stage: build
before_script:
- bundle config set path 'vendor/cache'
- bundle install
script:
- bundle exec jekyll build --future
artifacts:
paths:
- _site
expire_in: 4h
when: always
only:
- master
deploy:
stage: deploy
image: python:latest
script:
- pip install awscli
- aws s3 sync --delete _site/ s3://${S3_BUCKET}
- aws cloudfront create-invalidation --distribution-id ${CLOUDFRONT_DISTRIBUTION_ID} --paths '/*'
artifacts:
paths:
- _site
when: always
only:
- master
Setup Gitlab Server
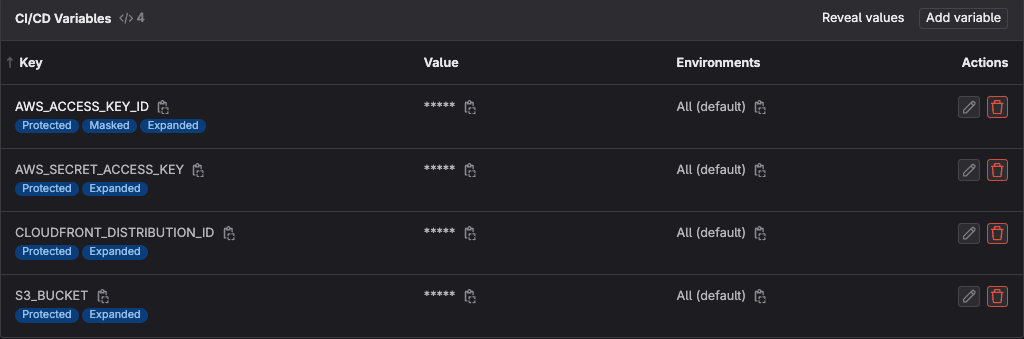
- Open the blog repo in gitlab. Go to Settings → CI/CD → Variables
- Enter the required variables by the CI/CD pipeline to deploy the site to S3. Make sure to mask and protect the secrets.
- AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID
- AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY
- CLOUDFRONT_DISTRIBUTION_ID
- S3_BUCKET
Push code to deploy site
Once the code is commited, pushed, and merged into the master/main branch, the gitlab ci jobs should start the deploy process to S3. Monitor the deployment under Build → Jobs
This post is licensed under
CC BY 4.0
by the author.